” I look at this new methane data as a disturbing early harbinger that maybe things might be worse than our global warming models predict.”
– Ken Caldeira, Ph.D., Carnegie Institution, Stanford University
September 9, 2006 Stanford, California – As we begin September 2006, there is more disturbing news about Earth’s environment. A rapidly spreading fungal disease is predicted to wipe out about half the world’s frogs, toads, newts and salamanders by the end of this year. Andrew Blaustein, a zoology professor at Oregon State University, says, “Species are going extinct very fast. These are bio indicators that something is wrong with the planet.”
The Australian Government Department of Environment reports, “Chytridiomycosis is an infectious disease that affects amphibians worldwide. It is caused by the chytrid fungus (Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis), a fungus capable of causing sporadic deaths in some amphibian populations and 100% mortality in others. The disease has been implicated in the mass die-offs and species extinctions of frogs in the past 15 years, but its origin and its true impact on populations remain uncertain and are under investigation.

“First discovered in dead and dying frogs in Queensland in 1993, chytridiomycosis is a highly infectious disease of amphibians, caused by the amphibian chytrid fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis. Research since then has shown that the fungus is widespread across Australia and has been present in the country since at least 1978. It is also found in Africa, the Americas, Europe, New Zealand and Oceania.”
Amazon Rainforest Threatened by Drought
Severe drought has been affecting the world’s largest rainforest in the Amazon of Brazil for the second year. Some scientists warn that “global warming and deforestation are pushing the entire enormous area towards a tipping point, where the rainforest could start to die.” Tree and plant deaths in the Amazon rainforest could release huge volumes of carbon dioxide into the Earth’s atmosphere, making greenhouse warming even worse.

Starvation Occurring As Global Warming Forces Ecosystems to Change Rapidly

The last two days of August, hundreds of dead seabirds known as shearwaters washed up on the beaches of Unalaska Island southwest of Fairbanks, Alaska, between the Bering Sea and Pacific Ocean. Even more dramatically, several hundred shearwaters fell dying or dead onto a crabbing boat in Unalaska Bay. Seabird specialist, Art Sowls, from the Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Refuge, told authorities that shearwaters can move in flocks of more than a million birds at a time. Sooty shearwaters migrate nearly 40,000 miles (64,000 kilometers) a year, flying from New Zealand to the North Pacific Ocean every summer in search of food, according to a new study.
Art Sowls wondered if the seabirds might be suffering from starvation. A few of the dead birds are undergoing necropsies and Art Sowls told me he hopes to have lab results back by mid-September. If the answer is starvation, could it be related to the rapidly warming Arctic climate that is causing permafrost to melt and forcing animals and their ecosystems to keep moving north in order to find familiar food sources?
Siberia and Arctic Permafrost Melting

Now this week in the September 7, 2006, issue of the journal Nature, Prof. Katey Walter from the University of Alaska at Fairbanks published data that shows the Arctic permafrost – especially in Siberia – is melting faster – and releasing five times more methane – than originally calculated. Methane is another greenhouse gas, but can trap heat 23 times more powerfully than carbon dioxide because methane absorbs solar radiation in a different spectrum than CO2.

What exactly is permafrost? When the last Ice Age glaciers were around some 20,000 years ago, dust and organic material got blown around on the soil in Siberia and Arctic tundra. The dust and organic material built up to at least 80 feet thick where it has been frozen ever since. Until this new modern era of global warming.
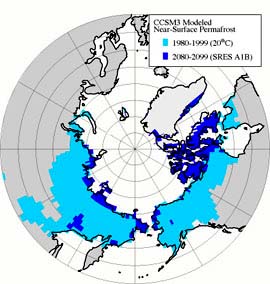
As the Earth warms up, the permafrost soils begin to melt and become wet. Microbes start to eat the carbon-rich organic material and use up oxygen as they consume the carbon. The result is that the carbon in the watery permafrost gets converted to methane, which is CH4. That’s one carbon molecule and four hydrogen molecules. That methane gas from all the carbon-digesting microbes bubbles up through melted water on the surface of permafrost and into the atmosphere. The warmer the Earth gets, the faster the permafrost melts, the more methane is added to the atmosphere, the thicker the methane and carbon dioxide blanket around the Earth becomes, which heats up Earth even more. Scientists call it a “positive feedback” cycle and methane could threaten the world’s future climate even more by accelerating global heating.
One atmospheric scientist, who spent twelve years studying global warming computer models at Lawrence-Livermore Laboratory in California, is now a staff scientist at the Carnegie Institution’s Department of Global Ecology in Stanford University. He is Ken Caldiera, Ph.D. This week he explained that the Earth’s permafrost is supposed to have at least 900 billion tons of methane. That’s 150 tons of methane for every man, woman and child in the 6 ½ billion people on our planet. The fact that the Ice Age soils are now suddenly melting in more volume and speed than anyone ever expected disturbs Dr. Caldiera greatly.
Interview:
Ken Caldeira, Ph.D., Staff Scientist, Carnegie Institution, Department of Global Ecology, Stanford University, Palo Alto, California: “The frozen ground is 80 feet thick on average in Siberia. So, as soon as you heat the planet to a certain extent, it’s like we have a fuse burning down into the permafrost and releasing methane as it goes. So, what we might be doing over the next decades potentially could push us back some kind of tipping point where that would result in the release of most, or all of, the methane in permafrost soils.
IS THERE ANY COMPUTER SIMULATION ABOUT WHAT WOULD HAPPEN TO SURFACE LIFE IF ALL THE METHANE WERE RELEASED?
In our computer simulations of just fossil fuel burning without methane, we get temperature increases in the Arctic region of 20 degrees Celsius warming (68 degrees F.). When you get that kind of warming, definitely the methane will go (from permafrost melting). We’re looking at the kind of planet that has not existed for 50 million years.
GOING BACK TO THE DINOSAURS, REALLY.
Yes, or maybe the period shortly after the dinosaurs. But certainly what we’re doing to this planet is unusual even when viewed from a geologic perspective. For example, current data suggests that the Earth has never had more greenhouses gases in its atmosphere as it has now for at least 20 to 25 million years – and possibly 50 million years.
The other thing is that both the carbon dioxide – and methane after it converts to carbon dioxide – dissolves into the oceans. CO2 when it dissolves into seawater makes the ocean more acidic and can prevent marine organisms from building their shells and skeletons. So we are looking at a wide array of potential environmental catastrophes that we barely understand.
AND ARE REALLY COMING UPON US QUICKLY.
Yes, I think there is a sense of urgency. Katey Walter and her co-workers (Univ. of Alaska, Fairbanks) did a very thorough job of sampling the methane bubbles that were coming up through the lakes that formed in the permafrost. As the permafrost melts, the ice was turning to water and forming lakes. They (scientists) would put little devices to measure the bubbles and measure the amount of methane coming out. They did a sampling technique where they had some of the bubbling bubble catchers distributed randomly and some distributed over hot spots where they saw bubbles coming out vigorously.
By having the random sampling component, they could make better extrapolations from their measurements to what the average methane release was over the lakes. Then they were able to use satellite photographs and other aerial type materials to understand the size of these lakes have been growing over time. The main advance that gave them the higher estimate was a more thorough and careful set of measurements of the methane bubbling out of the water.
HOW SURPRISED ARE YOU AND OTHER SCIENTISTS THAT YOU KNOW THAT WITH THIS MORE THOROUGH MEASYUREMENT THAT IT IS NOW APPARENTLY CLEAR THAT FIVE TIMES THE AMOUNT OF METHANE IS BEING RELEASED?
I look at this new methane data as a disturbing early harbinger that maybe things might be worse than our global warming models predict. I mean this is coming up repeatedly. There were models of how much sea ice should melt back as a result of global warming and the satellite observations show that sea ice in the Arctic is melting back much faster than previously assumed. There is other evidence that Greenland is melting faster than a lot of models predicted. Here we have observations that suggest the permafrost is melting and releasing its methane faster than we had thought.
So, there is a whole series of observations where things are looking worse than had been anticipated before. It’s getting to the point where finding out things are worse than you thought is no longer surprising – that there seems to be a general trend of results that suggest that the early ideas about what the effects would be of global warming would be have turned out to be rather optimistic outlooks on the future.
IF THE METHANE FEEDBACK BEGINS TO ACCELERATE BECAUSE OF GLOBAL WARMING, WHAT IS THE WORST CASE IF THIS NOW FIVE TIMES AS MUCH METHANE AS THEY THOUGHT KEEPS INCREASING OVER THE NEXT QUARTER CENTURY? WHAT IS THE WORST CASE FOR SURFACE LIFE WITH THIS MUCH METHANE BEING ADDED TO THE BLANKET AROUND THE EARTH?
If current emission trends continue, the temperature bands – you can think of it as the Earth warms in bands of climate or temperature moving toward the poles. Already those bands are moving ten to twenty feet per day on average and under middle of the road kind of emission scenarios, those bands start moving 30 feet per day toward the poles.
Maybe it will end up being 40 or 45 feet a day and ecosystems need to move to keep up with their climate zones. And it’s obvious that oak trees and other sedentary organisms cannot move that fast to keep up with climate change. So, what will happen is that organisms will die off in climate zones they are no longer adapted to. Invasive species will come in and occupy those ecological niches.
So, I think what we will see is a replacement of the complex life that has developed over many millennia and millions of years and be replaced by a much weedier world. I think the future will be a great place for weeds and we will see a much weedier world.
People say, ‘Hasn’t climate changed in the past?’ If you look at the change from the glacial time to after the Ice Age ended, the current climate is changing about 100 times faster than it changed during the end of the glacial time. Carbon dioxide is increasing in the atmosphere about 100 times faster than it did in the last Ice Age.
My perspective is that we are so far – our industrial society has so overwhelmed natural emissions (of CO2) that we are far outside the capacity of the natural system to keep up with the rate of change that we are asking Earth to undergo.
DOES THAT MEAN THAT THE NUMBERS OF EXTINCTIONS WILL BE EVEN GREATER THAN HAS BEEN PROJECTED?
Yes. The ecosystems will have to move towards the poles at 30 feet a day in order to keep up with the climate change. First, that’s hard enough to do if you have a complete band of natural vegetation going from the equator to the poles. But in real life, that ecosystem has to cross roads and farm roads and cities and towns and then ump to some other place where it could possibly adapt to the new climate. If you take that oak tree that has an acorn that depends on a squirrel to run and bury that acorn somewhere. So maybe if the lifetime of that oak tree is 50 years and that squirrel can run a few hundred feet with the nut, it might be able to move a few hundred feet in 50 years.
That’s why I think what we are likely to see in the future is a world of weeds where weeds replace the kind of complex ecosystems that are more common today.
IS THERE ANYTHING THAT COULD BE DONE NOW THAT COULD EFFECT, OR STOP, THE TIPPING POINT IN THE INCREASING METHANE RELEASE?
OK, I think there are two basic strategies. The first strategy involves just diminishing greatly CO2 emissions, which requires a transformation of our energy systems.
The other possibility that has been discussed, although nobody has published detailed calculations about it is it might be able to inject aerosols in the stratosphere to block some sunlight and engineer our climate to prevent additional Arctic warming – or even cool the Arctic.
It’s one thing to add CO2 into the system and inadvertently be changing climate. The politics, ethics and wisdom of purposefully engineering our climate is a far more dubious matter. But it looks like it would be within our technical capability to engineer our climate directly. The question is: Do we have the wisdom to actually do that without creating even bigger problems.
IF WE DON’T DO EITHER, WHAT IS THE WORST CASE FOR THE FUTURE WITH METHANE BUILDING UP?
Nobody can really predict the future. But I think.. to me it looks like we are pushing our planet into territory it has not been for many tens of millions of years. When you give the planet that hard a knock, I don’t think anybody can accurately predict what is going to happen.
OUT: “Nobody can really predict the future. But to me it looks like we are pushing our planet into territory it has not been for many tens of millions of years. When you give the planet that hard a knock, I don’t think anybody can accurately predict what is going to happen.”
Climate Models Must Now Be Changed to Add New Methane Data
One of the most surprising facts I learned from Dr. Caldeira is that neither of the atmospheric computer models at the National Center for Atmospheric Research in Boulder, Colorado, nor the Lawrence-Livermore Laboratory in Livermore, California, have included increasing methane emissions in their atmospheric calculations.
Solutions to slowing down global warming include curtailing dependence on fossil fuel greenhouse emissions. This week former astronaut and U. S. Senator from New Mexico, Harrison Schmitt, told lawyers at an Albuquerque Bar Association meeting that we need quickly to get back to the moon to ensure humanity’s energy future. He explained that in the dust on the moon is an element called Helium-3. There’s enough helium-3 on the moon to feed little sun-like fusion reactors on Earth for the foreseeable future. Senator Schmitt says there is already a political context that would allow mining helium-3 for a global energy system. That is the Outer Space Treaty of 1967 between the United States and the Soviet Union. That treaty prohibited nuclear weapons or military bases on the moon. It also prohibits any nation from claiming the moon or other celestial bodies as territory. But that 1967 treaty would not prohibit a private company from going to the moon to mine helium-3.
Competition for lunar resources will soon begin as nations such as Japan, China, India, Russia and the United States all plan to be back on the moon in this coming decade. Meanwhile, in another ten years, how much of the Amazon forest will have died or been cleared away – releasing tons of carbon dioxide into the Earth’s atmosphere? How much permafrost will have melted releasing tons of methane into the Earth’s atmosphere? How much warmer will the Earth be? How ferocious will storms be? And how many species will be forever gone from the air, the water and the lands of our planet?
More Information:
For further information about global warming, please see the reports below in the Earthfiles Archives:
- 08/23/2006 — Solar Cycle 24 – Headed for Intense X Flares by 2010-2012?
- 08/19/2006 — Repair of Earth’s Ozone Layer Has Slowed
- 07/18/2006 — 2006 – Hottest Year So Far in U. S. History
- 06/24/2006 — “High Confidence” Earth Is Warmest in 400 Years – Maybe Even 2,000 Years or More
- 04/08/2006 — Recent Caribbean Coral Reef Die-Off Biggest Ever Seen
- 03/17/2006 — Planet Earth’s Ice Melt
- 02/20/2006 — Mysterious Deaths of Whales in Mexico
- 11/18/2005 — Is the Sun Heating Up?
- 10/07/2005 — Warmer Sea Surfaces and Increased Wind Power Are Making Hurricanes Stronger
- 09/29/2005 — 2005 Arctic Summer Ice Melt – Largest On Record
- 09/23/2005 — Phenomenon of “Instant” Hurricanes in 2005
- 09/23/2005 — 9 X-Class Solar Flares Between September 7 – 19, 2005.
- 08/26/2005 — What Is Killing Amphibians Around the World?
- 08/26/2005 — Another Cattle Mutilation in Canada
- 08/18/2005 — Unusual Summer Swarm of Arkansas Copperheads
- 08/05/2005 — Scientists Puzzled by “Bizarre” Pacific Coast Die-offs in 2005
- 05/11/2005 — Greenland Sea Cold Water Re-Cycling Has Nearly Stopped. Britain Expected to Become Cooler.
- 02/26/2005 — Collapse of Societies: From Easter Island to Iraq – to Western World?
- 02/03/2005 — British Scientists Warn Global Temperatures Could Climb Higher Than Earlier Estimates.
- 01/22/2005 — From U. S. to Arctic – A Sea Change in the Weather
- 12/31/2004 — Abrupt Climate Change Occurred Worldwide 5,200 Years Ago
- 11/02/2004 — North Pole Summers Without Ice?
- 10/15/2004 — Ever-Increasing Carbon Dioxide Build-Up in Atmosphere Since 1958
- 09/17/2004 — Cat 4 and 5 Hurricanes Charley, Frances and Ivan in Four Weeks -Unprecedented in American Recorded Weather History
- 08/27/2004 — Global Warming Impact On Birds – More Extinctions Expected
- 08/14/2004 — Oceans Are Absorbing A Lot of Greenhouse CO2. As Chemistry Changes, What Happens to Sea Life?
- 08/01/2004 — Sixth Straight Year Hundreds of Birds Die at Roestler Lake, North Dakota.
- 06/25/2004 — Wild 2, An Amazing Comet
- 06/07/2004 — Mayan Priest in Guatemala Writes About Rare Venus Transit
- 04/26/2004 — Update About Microbiologist Dan Burisch, Ph.D.
- 02/27/2004 — Abrupt Climate Change: Scenario from A Pentagon-Commissioned Report
- 02/23/2004 — Is There Liquid Water on Martian Surface?
- 01/02/2004 — Earth’s Speeded Rotation Puzzles Scientists
- 11/29/2003 — Glaciers Are Melting Around the World So Fast That Water Supplies Could Be Threatened
- 10/29/2003 — Fifth Intense Solar X-Flare – What’s Happening On the Sun?
- 05/30/2003 — Scientists Surprised by Common House Fly Fossils in Antarctica
- 01/05/2003 — What Are the Grooves in the Martian South Pole?
- 12/14/2002 — Arctic Rivers’ Fresh Water Flows Could Change Atlantic Ocean Current
- 11/14/2002 — What Happened 12,000 Years Ago That Killed So Many Animals?
- 10/21/2002 — Mt. Kilimanjaro’s Ice Cap Is Melting Fast
- 08/27/2002 — August 2002: Severe to Moderate Drought in 37 States
- 07/20/2002 — Extinctions of Earth Life Are Accelerating Rapidly
- 06/04/2002 — EPA Admits Humans Burning Fossil Fuels A Big Factor in Global Warming
- 03/30/2002 — Drought Worsens in United States
- 03/21/2002 — Antarctic Peninsula Is Melting – And So Is Arctic Ice
- 02/13/2002 — January 2002 Warmest On Record For Whole World
- 01/30/2002 — Latest Satellite Data Shows Surprisingly Thicker Ross Ice Shelf in Antarctica
- 01/05/2002 — Global Warming Update – Could Increasing Carbon Dioxide Gas Be Transformed Into Limestone?
- 12/22/2001 — Scientists Warn That Climate and Earth Life Can Change Rapidly
- 06/09/2001 — Environmental Updates and Colt Mutilated in Leitchfield, Kentucky
- 05/25/2001 — Federal GAO Report Does Not Rule Out Cell Phone Dangers
- 04/18/2001 — April Environmental Updates
- 03/24/2001 — Alps Permafrost Melting
- 03/21/2001 — Earth Hasn’t Been This Warm Since the Pliocene 3 Million Years Ago
- 03/04/2001 — Disappearing Glaciers – Evidence of A Rapidly Warming Earth
- 02/25/2001 — Environmental Updates
- 02/18/2001 — Environmental Updates and Mysterious Deaths of 2000 Atlantic Brant Geese
- 02/07/2001 — 94% Decline In Aleutian Islands Sea Otter Population
- 01/28/2001 — U. N. Global Warming Forecast: Up to 10.5 Degrees F. Hotter At End of 21st Century
- 01/07/2001 — Dinosaur-Killing Asteroid Punched 22 Miles Through Earth’s Entire Crust
- 11/26/2000 — Environmental Updates
- 10/30/2000 — Science, Environment and Medical Updates
- 09/10/2000 — Arctic Ice Melt Threatens Polar Bears
- 09/10/2000 — Largest-Ever Antarctic Ozone Hole
- 07/09/2000 — The “Cell from Hell” Is Back in North Carolina Estuaries
- 07/02/2000 — Brown Tide Devastating Long Island’s Great South Bay Shellfish
- 06/17/2000 — Spring 2000 – Hottest On Record in U. S.
- 05/07/2000 — Serious Drought in the Great Lakes
- 04/20/2000 — Severe Arctic Ozone Loss and Deep Ocean Warming
- 03/12/2000 — Environmental Updates and Mysterious Fires Near Scott, Arkansas
- 01/13/2000 — Computer Projections About Earth Weather 2000-2100
- 01/09/2000 — Global Warming Alert from NOAA and U.K.
- 12/25/1999 — Y2K Nuclear Concern and Global Warming Update
- 09/26/1999 — Could Ancient Microbes in Polar Ice Cause Epidemics?
- 07/25/1999 — Maryland Fish Kills; Global Warming; and Warm Oceans and Disease
- 06/04/1999 — Global Warming Linked to Increasingly Warmer and Wetter Winters in Europe & Western North America
- 05/05/1999 — Two Antarctic Ice Shelves Almost Gone
- 04/09/1999 — Strange Lights In Missouri
- 02/28/1999 — Chickadee Beak Deformities in Alaska
Websites:
Siberian Permafrost Melt: http://www.physorg.com/news5769.html
Arctic Permafrost Melt: http://news.mongabay.com/2005/1219-arctic.html
NOAA Global Warming Info: http://lwf.ncdc.noaa.gov/oa/climate/globalwarming.html
U. S. Global Change Research Program:
http://www.usgcrp.gov/usgcrp/nacc/education/alaska/ak-edu-3.htm
© 1998 - 2024 by Linda Moulton Howe.
All Rights Reserved.

