"This is the first time we have detected dark matter as having a
unique structure that is different from both the gas and galaxies in the cluster."
- M. James Jee, Ph.D., Astronomer, Johns Hopkins University
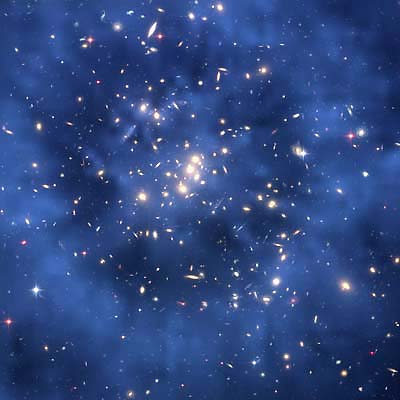

May 15, 2007 Baltimore, Maryland - The Hubble Space Science Institute reported today that astronomers using NASA's Hubble have discovered "a ghostly ring of dark matter that formed long ago during a titanic collision between two massive galaxy clusters.
"The ring's discovery is among the strongest evidence yet that dark matter exists. Astronomers have long suspected the existence of the invisible substance as the source of additional gravity that holds together galaxy clusters. Such clusters would fly apart if they relied only on the gravity from their visible stars. Although astronomers don't know what dark matter is made of, they hypothesize that it is a type of elementary particle that pervades the universe.
Click here to subscribe and get instant access to read this report.
Click here to check your existing subscription status.
Existing members, login below: